Research
-
Microbiomes have been described as ‘ecosystems on a leash,’ because immunological control of the microbiome is critical for host health. Variation in the genes that produce the immune system has been linked to microbiome dysbiosis and to disease, and studying immune systems in the context of host-microbe coevolution has generated critical insights. However, we do not understand the evolutionary forces maintaining host genetic variation related to the microbiome or how immune systems coevolve with beneficial microbes. We use aphids as a model insect system, along with techniques adapted from human innate immunology, functional and forward genetics, and dual-RNAseq of both host and microbes. We're interested in questions like:
How has coevolution with the microbiome contributed to genetic variation in the immune system?
Does adaptation to beneficial microbes trade-off with the ability to combat pathogens?
How does control of the microbiome shape microbial virulence?
-
Vertically-transmitted viruses are often hidden players affecting host phenotypes. There are a number of vertically transmitted viruses found across aphid species, especially in the subfamily Densovirinae, and viral genes have been frequently incorporated into aphid genomes. We’re using this system to study:
What function conserved endogenous viral elements serve in aphid genomes
How heritable viruses act as hidden drivers of insect evolution
-
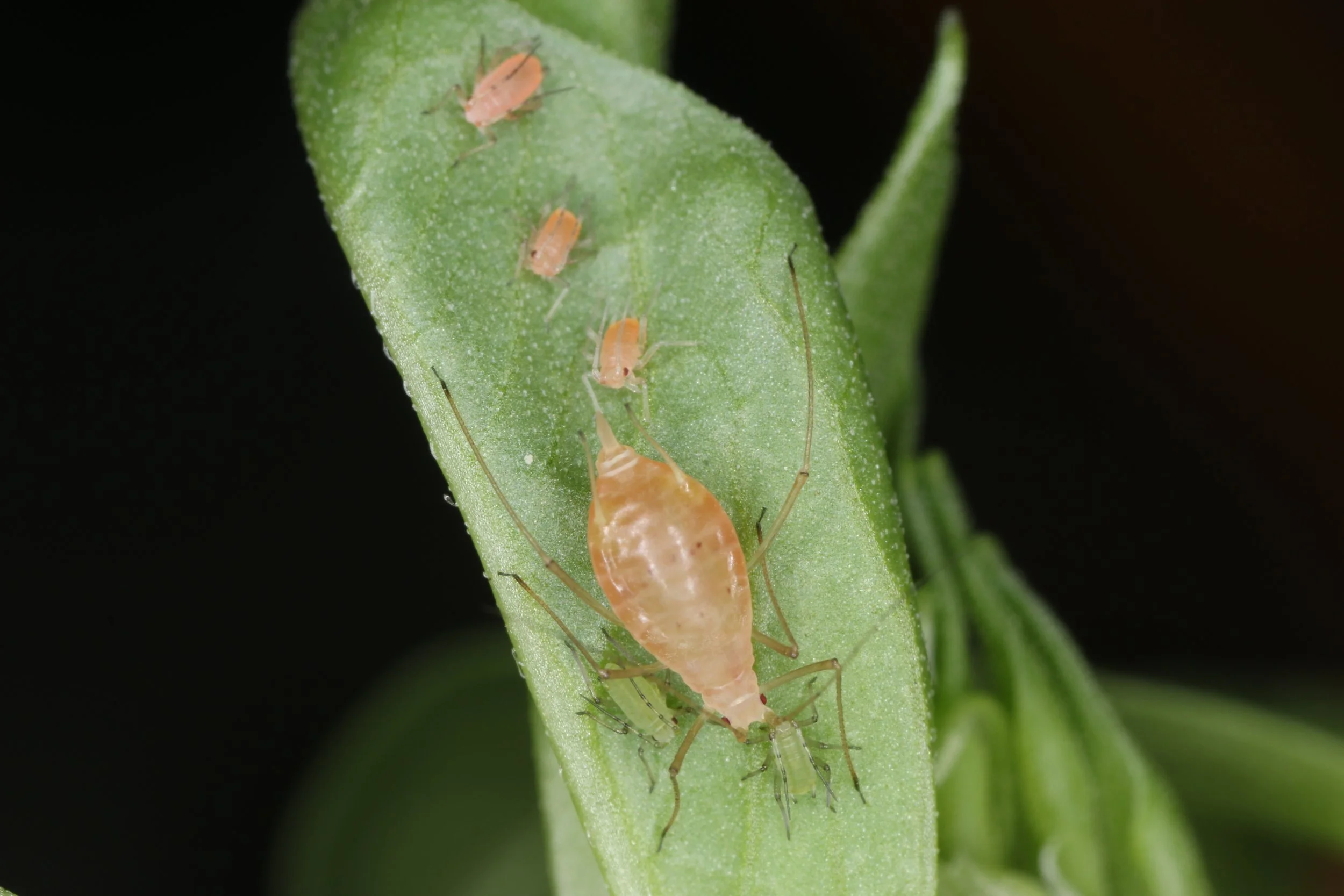
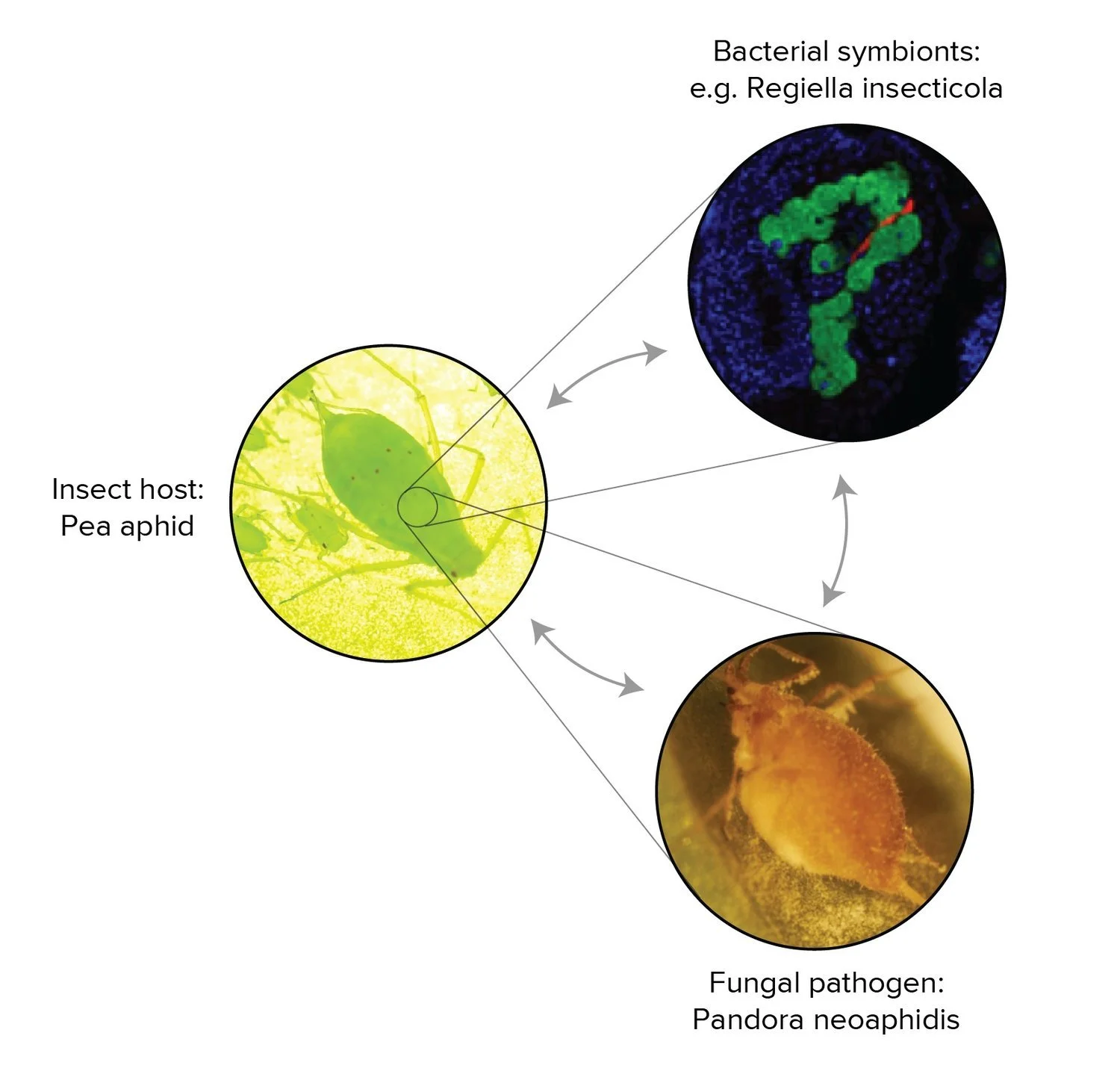
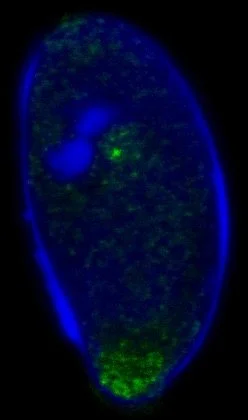
Animal-associated microbes often have specific phenotypic effects on their hosts—for example Regiella insecticola makes aphids resistant against an important natural enemy, the fungal pathogen Pandora neoaphidis. We are studying this three-way coevolutionary interaction to learn:
Why and how microbes protect their hosts from pathogens and what keeps ‘beneficial’ microbes from cheating
How symbiotic partners achieve specificity within and among species and what these patterns teach us about host-microbe coevolution
-
The biology of insects and their associated microbial communities can inform the control of medically and agriculturally relevant pest insects. For example, we're interested in:
What bacteria, fungi, and viruses are associated with bed bugs in hospital settings, and what role are these microbes playing in bed bug biology?
How do entomopathogenic fungi kill insect pest species, and can these mechanisms be harnessed for biocontrol?
Publications
Rozo-Lopez, P., Torres, V., Torres, J., Drolet, B.S., Kafer, S., & Parker, B.J. (2025) Heritable viral symbionts in the family Iflaviridae are widespread among aphids. In Press, Applied and Environmental Microbiology. biorXiv.
Parker, B.J. & Rozo-Lopez, P. (2025) Heritable viruses as hidden drivers of insect phenotypes and evolution. In Press, Annual Reviews of Entomology.
Adler, M.J., Martin, M.M., Rozo-Lopez, P., & Parker, B.J. (2025) A novel mitovirus associated with the fungal entomopathogen Zoophthora radicans infecting pea aphids. PLoS One, 20(9): e0331239.
Torres, J., Rozo-Lopez, P., Saleh Ziabari, O., & Parker, B.J. (2025) Draft genome sequence of the glasshouse-potato aphid Aulacorthum solani. Genes | Genomes | Genetics, 15(3): jkaf013.
Gregory, L.E., Driscoll, R.M.H., Parker, B.J., & Brisson, J.A. (2025) Impacts of body color, symbionts, and genomic regions on the pea aphid wing plasticity variation. Molecular Ecology, 34(5): e17660.
Brewer, S.,* Adler, M.J., Martin, M.M.,* Rozo-Lopez, P., & Parker, B.J. (2025) Novel viruses in the families Iflaviridae and Partitiviridae associated with the common eastern firefly Photinus pyralis. MicroPublication Biology, 10.17912/micropub.biology.001385.
Kolp, M.R., de Anda Acosta, Y.,* Brewer, W., Goldstein, E.B., Nichols, H.L., & Parker, B.J. (2024) Pathogen-microbiome interactions and the virulence of an entomopathogenic fungus. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 90(6).
Rozo-Lopez, P., Brewer, W., Käfer, S., Martin, M.M.,* & Parker, B.J. (2023) Untangling an insect’s virome from its endogenous viral elements. BMC Genomics, 24(636).
Rozo-Lopez, P. & Parker, B.J. (2023) Why do viruses make aphids winged? Insect Molecular Biology, 32(6): 5575-582.
Goldstein, E.B., de Anda Acosta, Y.,* Henry, L.M., & Parker, B.J. (2023) Variation in density, immune gene suppression, and co-infection outcomes among strains of the aphid endosymbiont Regiella insecticola. Evolution, 77(7): 1704-1711.
Inchauregui, R.A.,* Tallapragada, K., & Parker, B.J. (2023) Aphid facultative symbionts confer no protection against the fungal entomopathogen Batkoa apiculata. PLOS One, 18(5): e0286095.
Parker, B.J. (2021) Mechanisms and evolution of heritable microbial density in insect hosts. Invited Commentary, mSystems, 6(4): e00728-21.
Nichols, H.L., Goldstein, E.B., Saleh Ziabari, O., & Parker, B.J. (2021) Intraspecific variation in immune gene expression and heritable symbiont density. PLOS Pathogens, 17(4): e1009552..
Parker, B.J., Driscoll, R.M.H., Grantham, M.E., Hrcek, J., & Brisson, J.A. (2021) Wing plasticity and associated gene expression varies across the pea aphid biotype complex. Evolution, 75-5: 1143–1149.
Parker, B.J., Hrcek, J., McLean, A.H.C., Brisson, J.A., & Godfray, H.C.J. (2021) Intraspecific variation and within-host density in an insect-microbe symbiosis. Molecular Ecology, 30: 1559-1569.
Li, B., Bickel, R.D., Parker, B.J., Saleh Ziabari, O., Lui, F., Vellichirammal, N.N., Simon, J.-C., Stern, D.L., and Brisson, J.A. (2020) A large genomic insertion containing a duplicated follistatin gene is linked to the pea aphid male wing dimorphism. eLife, 9: e50608.
How a pea aphid decides to make wings or not - The Scientist
Chung, S.H., Parker, B.J., Blow, F., Brisson, J.A., & Douglas A.E. (2020) Host and symbiont genetic determinants of nutritional phenotype in a natural population of the pea aphid. Molecular Ecology, 29(4): 848-858.
McLean, A.H.C., & Parker, B.J. (2020) Variation in intrinsic resistance of pea aphids to parasitoid wasps: a transcriptomic basis. PLOS One, 15(11): e0242159.
Hammelman, R.E., Heusinkveld, C.L., Hung, E.T., Meineke, A.I., Parker, B.J., & Brisson, J.A. (2020) Extreme developmental instability associated with wing plasticity in pea aphids. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 287: 20201349.
McLean, A.H.C., Hrcek, J., Parker, B.J., Mathe-Hubert, H., Kaech, H., Paine, C. & Godfray, H.C.J. (2020) Multiple phenotypes conferred by a single insect symbiont are independent. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 287: 20200562.
Parker, B.J. & Brisson, J.A. (2019) A laterally transferred viral gene modifies aphid wing plasticity. Current Biology, 29: 2098-2103.
Virus genes help determine if pea aphids get their wings - Research News: National Science Foundation
‘Borrowed’ virus genes put wings on some pea aphids - Futurity
Reyes, M.L., Laughton, A.M., Parker, B.J., Wichmann, H., Fann, M., Sok, D., Hrcek, J., Acevedo, T., Gerardo, N.M. (2019) The influence of symbiotic bacteria on reproductive strategies and wing polyphenism in pea aphids responding to stress. Journal of Animal Ecology, 88(4): 601-611.
Hrcek, J.,* Parker, B.J.,* McLean, A.C.H., Simon, J.C., Mann, C., & Godfray, H.C.J. *Co-first authors. (2018) Hosts do not simply outsource pathogen resistance to protective symbionts. Evolution, 72-2: 1488-1499.
McLean, A.H.C.,* Parker, B.J.,* Hrcek, J., Kavanagh, J., Wellham, P.A.D., & Godfray, H.C.J. *Co-first authors. (2018) Consequences of symbiont co-infections for insect host phenotypes. Journal of Animal Ecology, 87: 478-488.
Parker, B.J., McLean, A.H.C., Hrcek, J., Gerardo, N.M., & Godfray, H.C.J. (2017) Establishment and maintenance of pea aphid endosymbionts after horizontal transfer is dependent on host genotype. Biology Letters, 13: 20170016. pdf
McLean, A.H.C., Hrcek, J., Parker, B.J., & Godfray, H.C.J. (2017) Cascading effects of herbivore protective symbionts on hyperparasitoids. Ecological Entomology, 42(5): 601- 609. pdf
Parker, B.J., Hrcek, J., McLean, A.H.C., & Godfray, H.C.J. (2017) Genotype specificity among hosts, pathogens, and beneficial microbes influences the strength of symbiont mediated protection. Evolution, 71(5): 1222-1231. pdf
Parker, B.J.,* Barribeau, S.M.,* Laughton, A.M., Griffin, L.H., & Gerardo, N.M. *Co-first authors. (2017) Life-history strategy determines constraints on immune function. Journal of Animal Ecology, 86(3): 473-483.
McLean, A.H.C., Parker, B.J., Hrcek, J., Henry, L.M., & Godfray, H.C.J. (2016) Insect symbionts in food webs. Invited Review, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 371: 20150325. pdf
Gerardo, N.M., & Parker, B.J., (2014) Mechanisms of symbiont-conferred protection against natural enemies: an ecological and evolutionary framework. Current Opinion in Insect Science, 4: 8-14. pdf
Parker, B.J., Garcia, J.R., & Gerardo, N.M. (2014) Genetic variation in resistance and fecundity tolerance in a natural host–pathogen interaction. Evolution, 68(8): 2421-2429. pdf
Garcia, J.R., Laughton, A.M., Malik, Z., Parker, B.J., Trincot, C., Chiang, S., Chung, E., & Gerardo, N.M. (2014) Partner associations across sympatric broad-headed bug species and their environmentally acquired bacterial symbionts. Molecular Ecology, 23(6): 1333-1347. pdf
Barribeau, S.M.,* Parker, B.J.,* & Gerardo, N.M. *Co-first authors. (2013) Exposure to natural pathogens reveals costly aphid response to fungi but not bacteria. Ecology and Evolution, 4(4): doi:10.1002/ece3.892. pdf
ter Braak, B., Laughton, A.M., Altincicek, B., Parker, B.J., Gerardo, N.M. (2013) Exposure to bacterial signals does not alter pea aphids’ survival upon a second challenge or investment in production of winged offspring. PLOS One, 8(8): e73600. pdf
Parker, B.J., Spragg, C.J., Altincicek, B., & Gerardo, N.M. (2013) Symbiont-mediated protection against fungal pathogens in pea aphids: a role for pathogen specificity? Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 79(7): 2455-2458. pdf
Parker, B.J., Barribeau, S.M., Laughton, A.M., de Roode, J.C., and Gerardo, N.M. (2011) Non-immunological defense in an evolutionary framework. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 26(5): 242-248. pdf
Gerardo, N.M., Altincicek, B., Anselme, C., Atamian, H., Barribeau, S.M., de Vos, M., Duncan, E.J., Evans, J.D., Gabaldón, T., Ghanim, M., Heddi, A., Kaloshian, I., Latorre, A., Moya, A., Nakabachi, A., Parker, B.J., Pérez-Brocal, V., Pignatelli, M., Rahbé, Y., Ramsey, J.S., Spragg, C.J., Tamames, J.S., Tamarit, D., Tamborindeguy, C., Vincent–Monegat, C., and Vilcinskas, A. (2010) Immunity and other defenses in pea aphids, Acyrthosiphon pisum. Genome Biology, 11(2): R21. pdf
Tiny aphid holds big surprises in genome - eScience Commons
The International Aphid Genomics Consortium. (2010) Genome Sequence of the Pea Aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLOS Biology, 8(2): e1000313. pdf
Parker, B.J., Elderd, B.D. and Dwyer, G. (2010) Host behaviour and exposure risk in an insect–pathogen interaction. Journal of Animal Ecology, 79(4): 863-870. pdf
*Indicates Parker Lab Undergraduate Researchers